Docker API Exposure via Tailscale VPN - Windows Setup Guide (with WSL2 Backend)
In last post, I’ve shown how to expose Docker’s API (port 2376) to your Tailscale VPN network on Linux systems. This post is a continuation of that guide, but for Windows with WSL2 backend.
Overview
This guide shows how to expose Docker’s API (port 2375) to your Tailscale VPN network on Windows with WSL2 backend. It’s a simple guide for those who want to use Docker remotely or access the status of Docker Containers from another device.
WARNING
We’re using port 2375 without SSL/TLS encryption. Thus, you need to use a VPN tunnel to provide encryption and access control.
Prerequisites
- Docker Desktop for Windows with WSL2 backend
- Tailscale VPN installed and running
- Administrator access to Windows
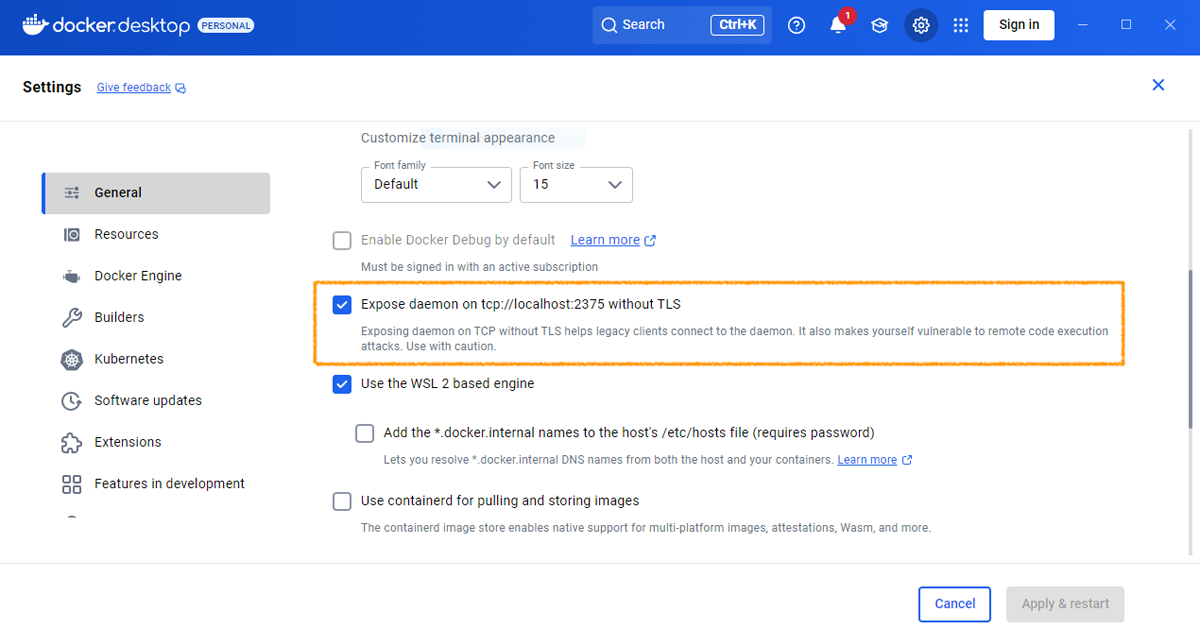
Step 1: Enable Docker API in Docker Desktop
- Open Docker Desktop
- Go to Settings → General
- Check “Expose daemon on tcp://localhost:2375 without TLS”
- Click Apply & Restart
Step 2: Find Your Tailscale IP Address
ipconfig
Look for the Tailscale adapter - note the IPv4 address (e.g., 100.xxx.xxx.xxx)
Step 3: Set Up Port Forwarding (Run as Administrator)
Open PowerShell as Administrator:
- Press
Win + X→ Select “Windows PowerShell (Admin)” - Or press
Win + R→ typepowershell→ pressCtrl + Shift + Enter
Run these commands:
:: Add port forwarding rule (replace with your Tailscale IP)
netsh interface portproxy add v4tov4 listenport=2375 listenaddress=100.xxx.xxx.xxx connectport=2375 connectaddress=127.0.0.1
:: Configure Windows Firewall (Optional but recommended)
netsh advfirewall firewall add rule name="Docker API Tailscale" dir=in action=allow protocol=TCP localport=2375
Step 4: Verify Setup
:: Check port forwarding rules
netsh interface portproxy show all
Expected output:
Listen on ipv4: Connect to ipv4:
Address Port Address Port
--------------- ---------- --------------- ----------
100.xxx.xxx.xxx 2375 127.0.0.1 2375
Step 5: Test Connection
From any device on your Tailscale network:
# Test Docker connection
docker -H tcp://100.xxx.xxx.xxx:2375 version
# Or test port connectivity
telnet 100.xxx.xxx.xxx 2375
Cleanup Commands (if needed)
:: Remove port forwarding rule
netsh interface portproxy delete v4tov4 listenport=2375 listenaddress=100.xxx.xxx.xxx
:: Remove firewall rule
netsh advfirewall firewall delete rule name="Docker API Tailscale"
Security Notes
- ⚠️ Warning: This exposes Docker daemon without TLS encryption
- ✅ Safe: Tailscale provides encrypted VPN tunnel
- 🔒 Access: Only devices on your Tailscale network can connect
- 💡 Tip: Tailscale IPs are usually stable and don’t change frequently
Usage Examples
Once configured, you can use Docker remotely:
# Set environment variable for easier use
export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://100.xxx.xxx.xxx:2375
# Now use Docker commands normally
docker ps
docker images
docker run hello-world
Troubleshooting
- Connection refused: Check if Docker Desktop is running
- Port not accessible: Verify firewall rules and port forwarding
- Permission denied: Ensure commands were run as Administrator
- Tailscale IP changed: Update port forwarding rule with new IP
Enjoy Reading This Article?
Here are some more articles you might like to read next: